Picture this: you’re staring at a spreadsheet with thousands of rows of data in a single column, and your boss needs it converted to CSV format for the quarterly report due in an hour. Sound familiar? Converting column data to CSV format is one of those essential skills that can save hours of manual work and prevent countless headaches in data management.
Whether you’re working with customer lists, inventory data, or financial records, knowing how to convert column to CSV efficiently can transform your workflow and boost your productivity. This comprehensive guide will walk you through multiple methods, tools, and best practices to master this crucial data transformation skill.
Key Takeaways

- Multiple conversion methods exist – from built-in spreadsheet features to specialized online tools and programming solutions
- Proper formatting is crucial – understanding CSV structure ensures your converted data works seamlessly across different platforms
- Automation saves time – learning efficient techniques can reduce manual work from hours to minutes
- Data validation matters – always verify your converted files to prevent errors in downstream processes
- Tool selection impacts results – choosing the right conversion method depends on your data size, complexity, and technical requirements
Understanding CSV Format and Column Data
What is CSV Format? 🤔
CSV (Comma-Separated Values) is a simple file format that stores tabular data in plain text. Each line represents a data record, and each record consists of fields separated by commas. This universal format makes data exchange between different applications seamless and efficient.
Here’s what a basic CSV structure looks like:
Name,Email,Phone
John Smith,[email protected],555-0123
Jane Doe,[email protected],555-0456
Why Convert Column to CSV?
Converting column data to CSV format offers several advantages:
- Universal compatibility across different software platforms
- Lightweight file size compared to proprietary formats
- Easy data import/export for databases and applications
- Simple structure that’s both human and machine-readable
- Version control friendly for tracking data changes
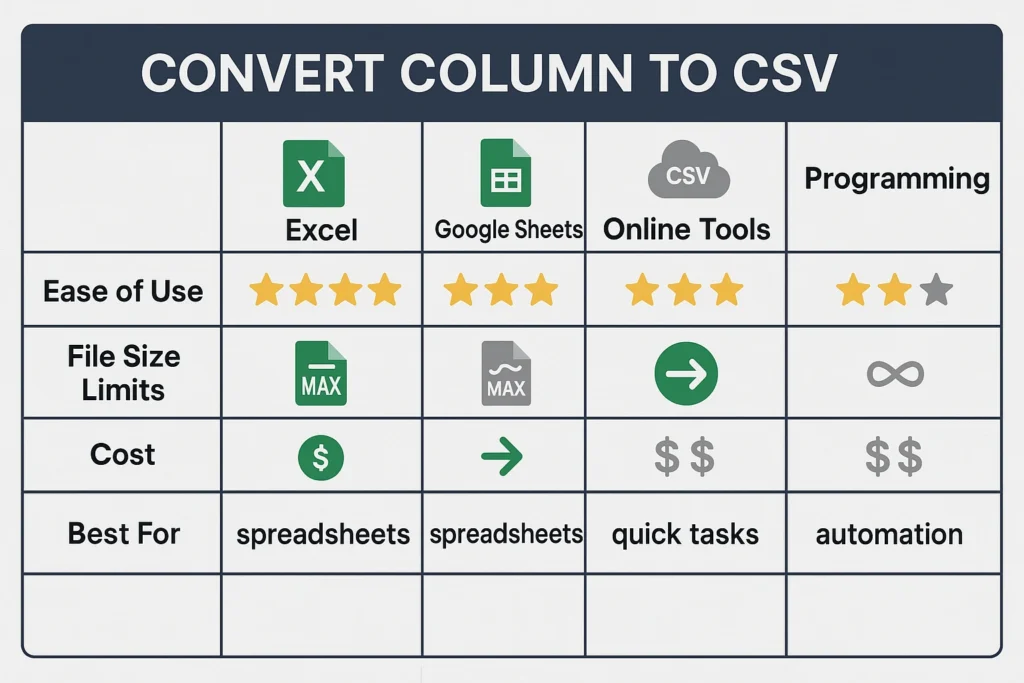
Methods to Convert Column to CSV
Method 1: Using Microsoft Excel 📈
Microsoft Excel provides the most straightforward approach to convert column to CSV format:
Step-by-Step Process:
- Open your data file in Excel
- Select the column(s) you want to convert
- Copy the selected data (Ctrl+C)
- Create a new workbook (Ctrl+N)
- Paste the data into the new sheet
- Navigate to File > Save As
- Choose “CSV (Comma delimited)” format
- Click Save and confirm the format
Pro Tips for Excel Conversion:
- Use “Save As” instead of “Export” for better control
- Check data preview before saving
- Handle special characters carefully
- Consider using “CSV UTF-8” for international characters
Method 2: Google Sheets Conversion 🌐
Google Sheets offers a cloud-based solution that’s perfect for collaborative work:
Conversion Steps:
- Upload or open your data in Google Sheets
- Select the target column(s)
- Copy and paste into a new sheet if needed
- Go to File > Download
- Select “Comma-separated values (.csv)”
- Save to your desired location
Google Sheets Advantages:
- Real-time collaboration
- Automatic cloud backup
- Cross-platform accessibility
- Built-in data validation tools
Method 3: Online CSV Conversion Tools 🔧
For quick conversions without installing software, online tools provide excellent alternatives. The comma separator tool offers specialized features for data transformation tasks.
Benefits of Online Tools:
- No software installation required
- Instant conversion capabilities
- Support for various input formats
- Often include data cleaning features
Method 4: Programming Solutions 💻
For advanced users handling large datasets, programming offers the most flexible approach:
Python Example:
import pandas as pd
# Read column data
data = pd.read_excel(‘input_file.xlsx’, usecols=[‘Column_Name’])
# Convert to CSV
data.to_csv(‘output_file.csv’, index=False)
R Example:
# Read data
data <- read.xlsx(“input_file.xlsx”)
# Select specific column
column_data <- data[, “Column_Name”, drop = FALSE]
# Write to CSV
write.csv(column_data, “output_file.csv”, row.names = FALSE)
Advanced Conversion Techniques
Handling Multiple Columns
When working with multiple columns, consider these strategies:
| Scenario | Best Approach | Tools Recommended |
| 2-5 columns | Manual selection in Excel/Sheets | Excel, Google Sheets |
| 6-20 columns | Spreadsheet with column mapping | Excel with formulas |
| 20+ columns | Programming solution | Python, R |
| Mixed data types | Specialized conversion tools | Data conversion tools |
Data Cleaning Before Conversion
Before you convert column to CSV, ensure your data is clean:
Common Issues to Address:
- Remove extra spaces and line breaks
- Handle null or empty values
- Standardize date formats
- Escape special characters
- Validate email addresses and phone numbers
Data Cleaning Checklist: ✅ Remove duplicate entries
✅ Standardize text case using text case converter tools
✅ Validate data formats
✅ Handle missing values
✅ Check for encoding issues
Dealing with Special Characters
Special characters can cause issues during CSV conversion:
Problem Characters:
- Commas within data fields
- Quotation marks
- Line breaks
- Non-ASCII characters
Solutions:
- Text qualifiers: Wrap fields in quotes
- Escape sequences: Use backslashes for special characters
- Alternative delimiters: Consider tab-separated values (TSV)
- Encoding specification: Use UTF-8 for international characters
Automation and Batch Processing
Setting Up Automated Workflows
For regular conversion tasks, automation saves significant time:
Excel VBA Solution:
Sub ConvertColumnToCSV()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ActiveSheet
‘ Select data range
ws.Range(“A:A”).Copy
‘ Create new workbook
Workbooks.Add
ActiveSheet.Paste
‘ Save as CSV
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs “output.csv”, xlCSV
End Sub
Benefits of Automation:
- Consistent formatting
- Reduced human error
- Time savings for repetitive tasks
- Scalability for large datasets
Batch Processing Multiple Files
When dealing with multiple files, consider these approaches:
- PowerShell scripts for Windows environments
- Bash scripts for Unix/Linux systems
- Python scripts for cross-platform solutions
- Dedicated batch processing tools
Quality Control and Validation
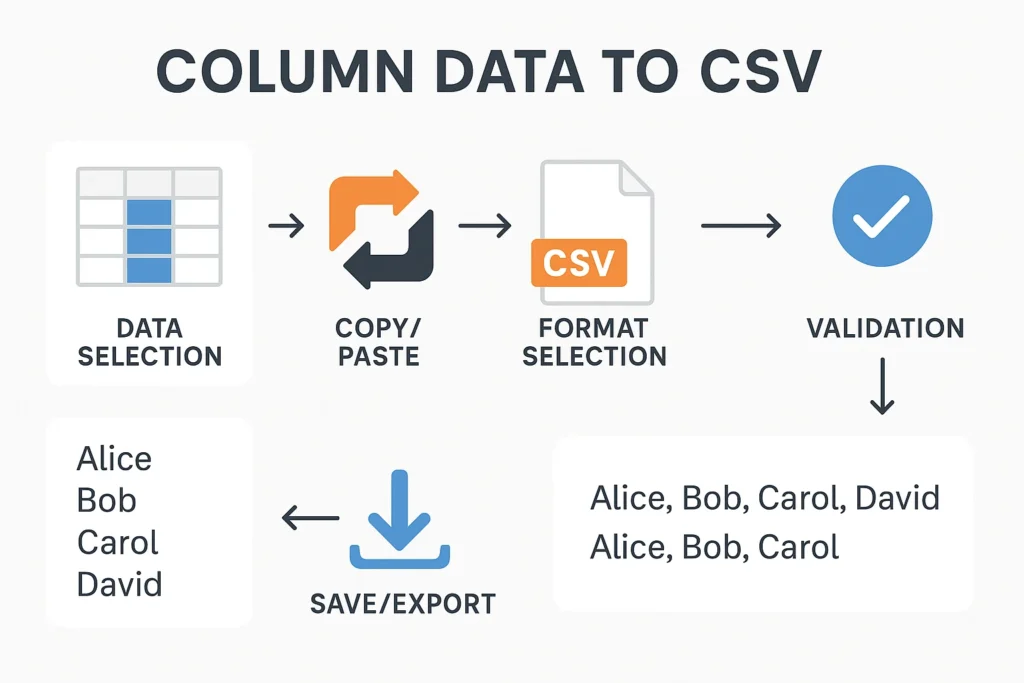
Verifying Conversion Results
Always validate your converted CSV files:
Validation Steps:
- Open in text editor to check raw format
- Import into different applications to test compatibility
- Compare row counts between source and output
- Spot-check data accuracy in random samples
- Test special characters and formatting
Common Conversion Errors
Watch out for these frequent issues:
Data Loss:
- Truncated long text fields
- Missing rows due to formatting errors
- Lost precision in numeric data
Format Problems:
- Incorrect delimiter usage
- Encoding mismatches
- Date format inconsistencies
Prevention Strategies:
- Always backup original data
- Use preview features before final conversion
- Test with small samples first
- Document conversion settings
Best Practices for CSV Conversion
File Organization and Naming
Establish consistent practices:
Naming Convention Examples:
- YYYY-MM-DD_dataset_name.csv
- project_data_v1.csv
- customer_list_cleaned.csv
Organization Tips:
- Create separate folders for raw and processed data
- Maintain version control
- Document conversion parameters
- Keep backup copies
Performance Optimization
For large datasets, optimize your conversion process:
Memory Management:
- Process data in chunks
- Use streaming methods for very large files
- Monitor system resources
- Consider cloud-based solutions for massive datasets
Speed Improvements:
- Use appropriate tools for data size
- Leverage multi-threading when available
- Optimize data types before conversion
- Remove unnecessary columns early
Troubleshooting Common Issues
File Size Limitations
Different tools have varying limitations:
| Tool | Maximum Rows | Maximum File Size | Best For |
| Excel | 1,048,576 | ~1GB | Small to medium datasets |
| Google Sheets | 10,000,000 cells | ~100MB | Collaborative work |
| Online tools | Varies | Usually <50MB | Quick conversions |
| Programming | Unlimited* | Unlimited* | Large datasets |
*Limited by available system resources
Character Encoding Problems
Encoding issues can corrupt your data:
Common Symptoms:
- Strange symbols in text
- Missing characters
- Import errors in target applications
Solutions:
- Use UTF-8 encoding when possible
- Specify encoding explicitly in conversion tools
- Test with international characters
- Consider text conversion tools for complex encoding issues
Import/Export Compatibility
Ensure your CSV files work across different platforms:
Testing Checklist:
- Import into Excel and Google Sheets
- Test with database systems
- Verify in text editors
- Check with target applications
Real-World Applications
Business Use Cases
Converting column to CSV is essential in various business scenarios:
Customer Relationship Management:
- Migrating contact lists between CRM systems
- Preparing data for email marketing campaigns
- Creating customer segmentation files
Financial Analysis:
- Converting transaction data for accounting software
- Preparing reports for profit calculation tools
- Creating budget tracking spreadsheets
Operations Management:
- Inventory data for warehouse systems
- Employee data for HR platforms
- Vendor information for procurement tools
Industry-Specific Examples
Healthcare:
- Patient data migration
- Insurance claim processing
- Medical record standardization
Education:
- Student enrollment data
- Grade book conversions
- Course catalog management
E-commerce:
- Product catalog updates
- Customer order history
- Inventory management systems
Advanced Tools and Techniques
Specialized Software Solutions
Beyond basic spreadsheet applications, consider these professional tools:
Data Integration Platforms:
- Talend Open Studio
- Apache NiFi
- Microsoft Power BI
- Tableau Prep
Database Management Tools:
- MySQL Workbench
- PostgreSQL pgAdmin
- Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio
- Oracle SQL Developer
API-Based Solutions
For automated, programmatic conversions:
REST API Benefits:
- Real-time data processing
- Integration with existing systems
- Scalable architecture
- Automated error handling
Implementation Considerations:
- Authentication requirements
- Rate limiting
- Error handling
- Data security
Future-Proofing Your Data Conversion Process
Emerging Standards and Formats
Stay informed about evolving data standards:
Next-Generation Formats:
- JSON for web applications
- Parquet for big data analytics
- Avro for schema evolution
- Arrow for in-memory processing
Migration Strategies:
- Plan for format transitions
- Maintain backward compatibility
- Document conversion processes
- Train team members on new tools
Technology Trends
Keep pace with technological developments:
Cloud-Based Solutions:
- Serverless data processing
- Managed ETL services
- Real-time streaming platforms
- AI-powered data cleaning
Machine Learning Integration:
- Automated data quality assessment
- Intelligent format detection
- Predictive data validation
- Smart error correction
Security and Privacy Considerations
Data Protection
When converting sensitive data, prioritize security:
Security Measures:
- Encrypt files during transfer
- Use secure cloud storage
- Implement access controls
- Audit conversion activities
Privacy Compliance:
- GDPR requirements for EU data
- CCPA compliance for California residents
- Industry-specific regulations
- Data anonymization techniques
Best Security Practices
File Handling:
- Use secure file transfer protocols
- Implement virus scanning
- Maintain audit trails
- Secure deletion of temporary files
Access Management:
- Role-based permissions
- Multi-factor authentication
- Regular access reviews
- Principle of least privilege
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Tool Selection Criteria
Choose conversion methods based on comprehensive evaluation:
Factors to Consider:
- Volume: How much data do you process regularly?
- Frequency: How often do you need conversions?
- Complexity: What level of data transformation is required?
- Budget: What resources are available for tools and training?
- Timeline: How quickly do you need results?
ROI Calculation:
- Time savings per conversion
- Reduced error rates
- Improved data quality
- Enhanced productivity
Investment Recommendations
Small Organizations:
- Start with free tools (Excel, Google Sheets)
- Invest in training for existing software
- Consider online conversion tools for occasional needs
Medium Organizations:
- Implement standardized processes
- Invest in dedicated data tools
- Train multiple team members
- Consider automation for frequent tasks
Large Organizations:
- Develop enterprise-grade solutions
- Implement comprehensive data governance
- Invest in specialized software
- Create dedicated data teams
Conclusion
Converting column to CSV is a fundamental skill in today’s data-driven world. Whether you’re using simple spreadsheet applications or sophisticated programming solutions, the key is choosing the right method for your specific needs and implementing proper quality control measures.
The techniques and best practices outlined in this guide provide a solid foundation for efficient data conversion. Remember that successful CSV conversion goes beyond just changing file formats – it’s about ensuring data integrity, maintaining compatibility, and creating sustainable workflows that can grow with your organization’s needs.
Next Steps to Master CSV Conversion:
- Start with your current tools – Practice basic conversion techniques using Excel or Google Sheets
- Experiment with online tools – Try specialized conversion utilities for different scenarios
- Develop standard procedures – Create documented workflows for common conversion tasks
- Build automation gradually – Implement scripts and automated processes for repetitive work
- Stay updated – Keep learning about new tools and techniques as technology evolves
By following these guidelines and continuously improving your data conversion skills, you’ll be well-equipped to handle any column-to-CSV conversion challenge that comes your way. Remember, efficient data conversion is not just about speed – it’s about accuracy, reliability, and creating processes that add real value to your organization’s data management capabilities.